Thursday 25 November 2010
BSM at ACIS 2010
Sunday 19 September 2010
Representation of Strategy Using i*-like Notation
Assessing and achieving alignment between an organization's strategies and its IT/business functions has long been recognized as a critically important question. This paper reports on a project that seeks to overturn established management orthodoxy by establising that strategies can be adequately modeled using conceptual modeling nota- tions and that methodological and tool support can be provided for the task of assessing and achieving alignment between the strategies of an organization and its service offerings. A key element of this enterprise has been the design of SML - the Strategy Modeling Language. This paper presents an interim report from this project that describes how a nota- tion inspired by i* has been used to obtain the diagrammatic modeling component of SML, and how i*-like notions have been used to represent strategy decomposition (required to be able to refine strategies to a level where there is an onotlogical match between the languages used to de- scribe strategies and services). We also comment on how i*-like notions would play a greater role in this project, as a complete model of the en- terprise context is brought to bear on the alignment exercise. We provide a brief illustration, and a description of the toolkit implemented on the Eclipse platform.
See here for more information.
Monday 13 September 2010
Identification and specification of relationships as the foundation for service bundling
See here for more information.
Thursday 9 September 2010
Service identification through value chain analysis and prioritization
In a resource constrained business world, strategic choices must be made on process improvement and service delivery. There are calls for more agile forms of enterprises and much effort is being directed at moving organizations from a complex landscape of disparate application systems to that of an integrated and flexible enterprise accessing complex systems landscapes through service oriented architecture (SOA). This paper describes the deconstruction of an enterprise into business services using value chain analysis as each element in the value chain can be rendered as a business service in the SOA. These business services are explicitly linked to the attainment of specific organizational strategies and their contribution to the attainment of strategy is assessed and recorded. This contribution is then used to provide a rank order of business service to strategy. This information facilitates executive decision making on which business service to develop into the SOA. The paper describes an application of this Critical Service Identification Methodology (CSIM) to a case study.
See here for more information.
Sunday 29 August 2010
Conceptualizing a bottom-up approach to service bundling
See here for more information.
Saturday 31 July 2010
Sourcing business and software services
In this paper, we address this need by discussing the relations between a comprehensive service lifecycle approach for service management & engineering and the sourcing & purchasing of services. In particular we pay attention to the similarities and differences between sourcing business and software services, the alignment between service management & engineering and sourcing & purchasing, the role of sourcing in the transformation of an organization towards a service-oriented paradigm, the role of architectural approaches to sourcing in this transformation, and the sourcing of specific services at different levels of granularity.
See here for more information.
Sunday 9 May 2010
Definition of a Description Language for Business Service Decomposition
See here for more information.
Sunday 11 April 2010
ACIS 2010 Track Service Engineering & Management
will be held in Brisbane, Australia, from 1-3 December 2010. ACIS is the premier conference in Australasia for Information Systems academics and professionals, covering technical, organisational, business and social issues in the application of Information Technology.
Submissions
ACIS 2010 calls for original, unpublished research papers (i.e. completed research and research-in-progress) in the areas defined in the conference track descriptions. All submissions must be in English and be made via the ACIS 2010 submission system at http://www.easychair.org/conferences/?conf=acis2010 by 12 July 2010. For more details about submission formats, expectations and the review process, please click here.
| Important Dates: | |
| Paper submission deadline: | 12 July 2010 |
| Notification of paper acceptance: | 17 September 2010 |
| ACIS 2010 Conference: | 1-3 December 201 |
Track Chairs:
Axel Korthaus
Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia
axel.korthaus@qut.edu.au
Tilo Böhmann
International Business School of Service Management Hamburg, Germany
boehmann@iss-hamburg.de
Erwin Fielt
Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia
e.fielt@qut.edu.au
Julien Vayssière
Smart Services CRC, Sydney, Australia
Julien.Vayssiere@smartservicescrc.com.au
Theme
Services dominate developed economies such as the USA, the EU, Australia, and others. This dominant position can not only be ascribed to the sheer size of the services sector in the overall economy, but also to the potential of services for creating economic growth and welfare through considerable opportunities for productivity gains. Moreover, it is not only business where a service perspective has become more prominent, also in IT the service concept has gained ground as is evident in developments like Services Sciences, Management, Engineering and Design (SSMED), IT Service Management, Service-Oriented Architectures (SOA), Service Computing and various “XYZas- a-Service” concepts. With business and IT becoming more and more aligned, there is a need for understanding how these two service worlds meet and to be aware of their complementarities and differences.
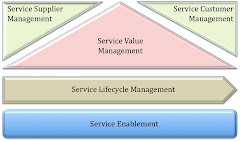
As the number of services grows and the differences between business and IT services blur, Business Service Management becomes crucial: the explicit management of these services as important business assets that are the focal points for the cost-effective creation of customer value and innovation in organisations. Business Service Management should leverage, integrate and complement the different Service Management approaches. From the IT perspective on Business Service Management, the paradigm of service orientation has been successfully applied on the technical level to design and implement very flexible and adaptable IT infrastructures and architectures for some time now. Service lifecycle management and service enablement approaches that aim towards implementing services as encapsulations of autonomous, valuable software capabilities are of importance in this context. However, this service paradigm recently also extends towards the business level and provides new perspectives to organise a company’s capabilities and to allow for the easy combination of services to create new business opportunities. In this sense, services can be seen as building blocks for organisational and market arrangements in service networks and ecosystems. On the business level, challenges related to the design of appropriate service value management, including service-enabled strategies, service-oriented business models, service portfolio
management, service governance etc. and service relationship management with suppliers and customers need to be met. Also on the business level, information technology represents one of the most important drivers and enablers of service innovation, and the service paradigm provides the opportunity for further advancing the widely postulated business/IT alignment.
Suggested topics
This track aims at accelerating high quality research in the fast developing domain of Service Management and Engineering and the related areas within Service Science (1) and Services Computing (2) from an Information System’s perspective. It seeks, in correspondence with the ACIS 2010 conference theme, contributions that demonstrate how the IS discipline can make a high impact in the academic and practical community by addressing the way organisations face the challenges of the progressing service-oriented economy that increasingly merges business- and IT-related service concepts. It invites conceptual and empirical papers on completed research as well as research-in-progress papers. Possible contributions may include, but are not limited to the following:
Service Management from an IS Perspective
- Service strategy & value management
- Service quality management
- Service innovation management
- Service portfolio & capability management
- Service governance & performance management
- Service compliance & risk management
- Service supply chain management
Service Engineering from an IS Perspective
- Service lifecycle
- New service development
- Service modelling, analysis & design
- Service bundling
- Service standards & descriptions
Special topics on Information Systems and Services
- The position of IS in Service Science, Management and Engineering
- New business models in service ecosystems, e.g. for service aggregation and brokerage
- IS/IT services from a service(-dominant) logic; servitisation of industries
- Implications of value co-creation for IT-based services
- Service business alignment / Aligning Business and IT Service Management
- Business impact of IT service management
- Embedding of IT services in business products and services
- Design and Implementation and effects of automation and self-service technologies for IT services
- Services E-commerce (i.e. electronic offering, trading, and purchasing of services)
Significance of this track and coverage at related outlets
Service management on both the business level and the IT level is a buzzing topic as is apparent in the increasing emphasis on the Service Economy, the promotion of Services Sciences, Management, Engineering and Design (SSMED) by IBM and others, the rise of Service Management in IT (e.g. ITIL v3), the developments in the area of Service-Oriented Architectures (SOA), and the growing importance of service as a sourcing model for software (e.g. Software-as-a-Service, SaaS). In Australia, services receive considerable attention in the research community, e.g. in the vation, foresight and productivity improvements for the services sector, as well as in the teaching community, e.g. the Services Science Management and Engineering (SSME) Learning and Teaching Project funded by the Australian Learning and Teaching Council. Service management starts to become addressed in a great variety of well-established and newly created, dedicated conferences and journals, such as ECIS, ICIS, AMCIS, ICSOC, APSCC, SCC, the German-language community IS conference (last event with 1200+ attending with conference theme “Business Services: Concepts, Technologies, Applications”) etc. and IBM Systems Journal, Business and Information Systems Engineering (BISE), Information Systems Management, Asian-Pacific Journal of Information Systems, among others. Moreover, the AIS has launched a special interest group for services, covering IT services, IT Service Management, and SSME.
List of Associate Editors
- Prof Gerhard Satzger, Director, Karlsruhe Service Research Institute (KSRI), Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- Prof Marlon Dumas (University of Tartu, Estonia)
- Assoc Prof Harry Bouwman (TU Delft, the Netherlands)
- Assoc Prof Aileen Cater-Steel (University of Southern Queensland, Australia)
- Dr Alistair Barros (SAP Research, Brisbane, Australia)
- Dr Timber Haaker (Novay, the Netherlands)
Potential journal special issue or awards
- Journal special issue
- We plan to give authors of the best papers in the ACIS 2010 Service Management and Design track the opportunity to submit an extended version of their work to a special issue of The Journal of Strategic Information Systems (JSIS).
- Best Paper in the Track Award
- We plan to ask the reviewers of paper submissions to suggest candidates for the best paper in the track. Based on this feedback, the winner of this award will be determined. The award for the best (“smartest”) track paper will be an iTunes gift card sponsored by the Smart Services CRC.
- Best Reviewer in the Track Award
- We plan to ask the authors of paper submissions to suggest candidates for the best reviewer in the track. Based on this feedback, the winner of this award will be determined.
Track chairs
Dr Axel Korthaus is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in QUT’s BPM Group, one of the largest BPM research groups in the world. He received his PhD degree in 2001 from the University of Mannheim, Germany, and brings to bear comprehensive experience as a researcher, lecturer and project manager in areas such as service management and collaborative, component-based software development. Besides managing and conducting research in an ARC Linkage project titled “Service Ecosystems Management for Collaborative Process Improvement”, which involves SAP Research Brisbane and the Queensland Government, Department of Public Works, as partners, Axel is also actively shaping the research conducted in the Smart Services CRC “Business Service Management” project. He is an author/editor of various books, journal articles and conference papers, serves as a regular PC member and speaker at IS- and SE-related conferences, organizes workshops and sessions and has presented his work in 11 countries over the last years.
Prof Tilo Boehmann is a Full Professor of Service Management at the International Business School of Service Management (ISS) in Hamburg, Germany. At ISS, he builds a new Service Management Research Group and the shapes the school’s MBA service management program after holding an appointment as research group leader and assistant professor at the Technische Universität München. His main teaching and research interests are service management and design, with a special interest in IT services and solutions, as well as strategic information management. Tilo has published widely in these areas in international and national journals and conferences. He is very active in the field of service science, management and engineering (SSME), being appointed member of a national service science task force of Germany’s federal ministry of research and education. Tilo holds a Habilitation from Technische Universität München (TUM), a PhD from Hohenheim University (Stuttgart, Germany) and a Master of Science in IS from the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dr Erwin Fielt is currently a senior researcher at the Business Process Management Group
of the Queensland University of Technology. In his research, he focuses on the intersection
between business and IT, where new IT applications have to result in net benefits for individuals and organisations. Erwin Fielt is involved as a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in the Business Service Management project of the Smart Services CRC. Within this project, he is responsible for coordinating the involvement of the different academic and industry partners and he conducts research on Service Management, Service Oriented Business Models, Service Portfolio Management and Service Quality. Erwin Fielt has a PhD from the Delft University of Technology and a MSc from the University of Twente, both in the Netherlands. He has published in different IS journals, conferences and books on services, business models, and electronic business.
Dr Julien Vayssière is Head of Research at the Smart Services CRC, a commercially focused collaborative research initiative, developing innovation, foresight and productivity
improvements for the services sector. Julien holds a PhD in Computer Science from the University of Nice, France and has been performing research on computer security and distributed software architectures for both industrial and academic organisations.
(1) See, for example, Pinhanez, C. and Kontogiorgis, P. (2008): A Proposal for a Service Science Discipline
Classification System. Presented at the 2008 Frontiers of Service.Washington, DC. October 2 -5, 2008 (Available
at http://www.smith.umd.edu/frontiers2008/pdfs_docs/Pinhanez.pdf)
(2) See, for example, Zhang, L-J. (2008): EIC Editorial: Introduction to the Knowledge Areas of Services Computing.
IEEE Transactions on Services Computing 1(2), 62-71.
Wednesday 31 March 2010
Towards a service portfolio management framework
See here for more information.